2024 Atlantic Hurricane Season Ends with Record Damage and Unprecedented Storms
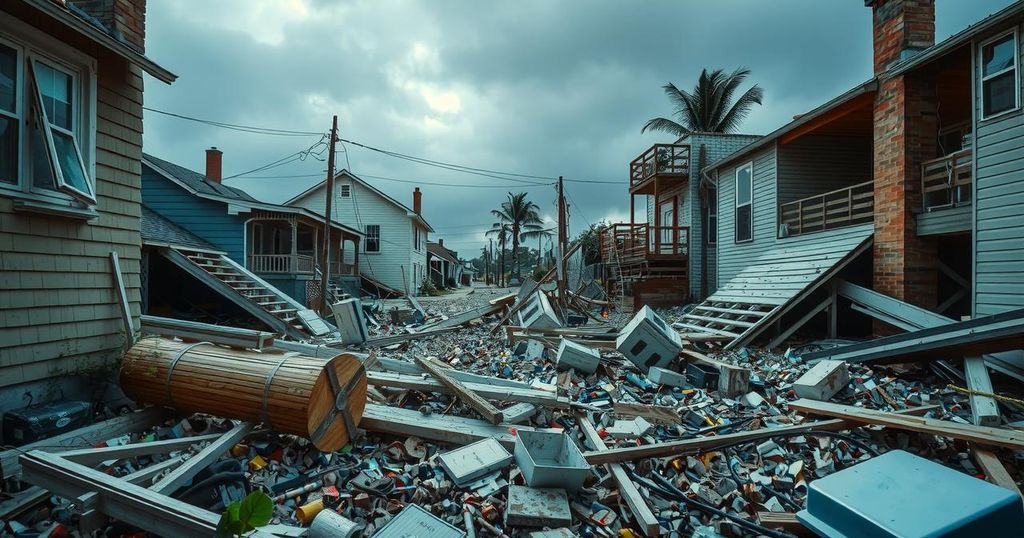

The 2024 Atlantic hurricane season concluded with an unprecedented 11 hurricanes, primarily influenced by unusually warm ocean temperatures. Significant storms such as Hurricane Helene and Hurricane Milton caused widespread destruction and fatalities in the U.S. The link between climate change and hurricane intensity remains a critical area of concern as meteorologists anticipate future trends in storm activity.
The 2024 Atlantic hurricane season concluded with 11 hurricanes, surpassing the average of seven, and left a trail of devastation across several regions far from the Gulf Coast. Meteorologists characterized this season as notably intense, largely due to elevated ocean temperatures. The season was marked by impactful hurricanes, including Hurricane Beryl, which became the first recorded Category 4 hurricane in June, causing significant damage in Grenada and Jamaica.
Hurricane Helene, which struck in September, resulted in over 200 fatalities and inflicted an estimated $48.8 billion in damages, primarily in North Carolina. It was the deadliest storm to affect the U.S. mainland since Hurricane Katrina. Furthermore, Hurricane Milton reached extraordinary wind speeds of 180 mph in October, positioning it among the strongest ever recorded in the Gulf of Mexico. This season also featured Hurricane Rafael, which nearly tied for the strongest November hurricane recorded in the Gulf.
The effects of climate change may be exacerbating the frequency and intensity of these storms, with unusually warm oceans contributing to unprecedented hurricane activity at atypical times of the year. Brian McNoldy, a hurricane researcher, stated, “… it certainly has its finger on the scale and makes these extreme storms more likely to occur.”
The Atlantic hurricane season typically runs from June 1 to November 30, with peak activity occurring from August to October. Each year, meteorologists analyze ocean temperatures, atmospheric conditions, and various climatic factors to forecast hurricane likelihood and intensity. The 2024 season has garnered attention due to an unusual increase in storm activity, with warmer ocean waters being partly attributed to the heightened frequency and strength of hurricanes. As climate change continues to influence global weather patterns, events like the 2024 hurricane season could serve as a harbinger of more extreme weather phenomena in the future.
In summary, the 2024 Atlantic hurricane season has been characterized by a significant increase in hurricane activity, with notable storms resulting in widespread devastation and loss of life. The correlation between warmer ocean temperatures and increased hurricane intensity raises important questions about the implications of climate change on future storm patterns. As experts continue to study these phenomena, it is essential to adopt strategies for mitigation and adaptation in vulnerable regions.
Original Source: wsvn.com