California Faces Extreme Weather Challenges Amid Climate Change Concerns
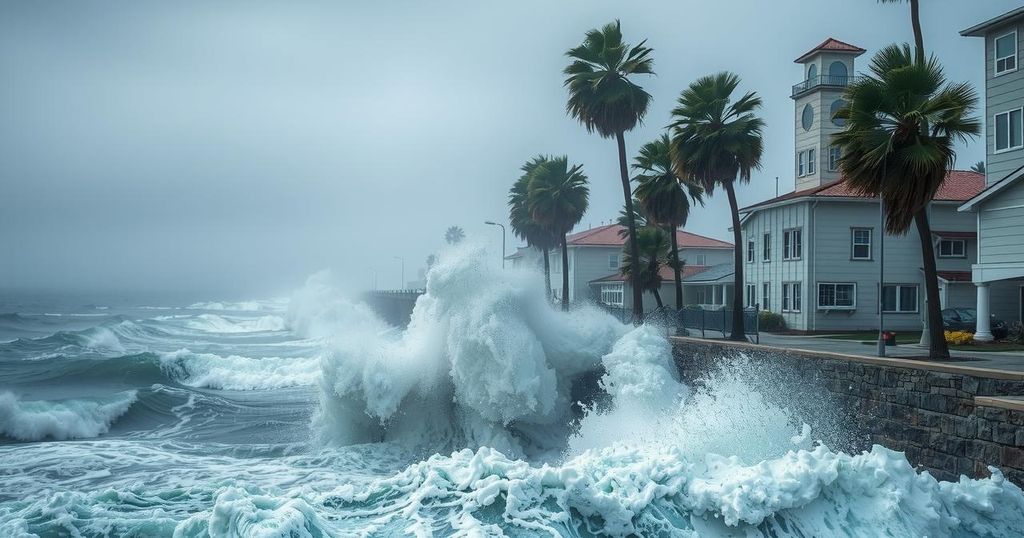

California is currently facing a series of extreme weather events, including hurricane-force winds, record rainfall, and a tornado warning in San Francisco. These patterns are associated with La Niña and climate change, leading to flooding and increased fire risks. The unusual combination of weather extremes represents the state’s vulnerability to significant atmospheric events this season.
Hurricane-force winds are currently impacting California, exacerbating a series of extreme weather events that have characterized recent weeks. In northern California, record rainfall of over twelve inches has been reported over a three-day span, alongside a fire prompting evacuation orders within Los Angeles County. Notably, a tornado warning was issued in San Francisco for the first time, highlighting the state’s susceptibility to unusual weather phenomena. Moreover, high surf advisories warned residents of waves potentially reaching 35 feet off the coast of Santa Cruz, where storm conditions have already caused significant damage.
Chandler Price, a meteorologist from the National Weather Service, noted that while these weather patterns align with La Niña conditions—typically leading to wetter weather in northern California—the occurrence of a tornado in the Bay Area is rare. The tornado did indeed cause destruction, overturning vehicles and damaging trees far from typical tornado regions. Despite the extreme conditions, meteorologists are observing significant snowfall in the Sierra Nevada as part of this winter’s storm cycle.
F. Martin Ralph, director of the Center for Western Weather and Water Extremes, attributed these persistent storms to climate change, which is believed to result in increased frequency of atmospheric rivers—long plumes of moisture that lead to heavy precipitation. He explained that while such storms are crucial for replenishing the state’s water supply, they can also produce disastrous flooding when excessive. Tragically, this week’s storms resulted in casualties and injuries due to debris flows and ocean-related incidents, further emphasizing the volatility of California’s weather systems.
California’s unique geography and climate make it particularly vulnerable to various weather extremes, which are increasingly influenced by climate change. The current weather events illustrate this volatility, with record rainfall leading to substantial flooding paired with high wind speeds and the accompanying risk of tornado occurrences. Furthermore, the contrasting drought conditions exacerbated by Santa Ana winds contribute to California’s fire hazards. Such extremes have become more frequent as atmospheric phenomena, like La Niña, intensify weather patterns in the region.
In conclusion, California is experiencing significant extreme weather events, driven by ongoing climate changes that heighten the frequency and intensity of storms. Record rainfall and destructive winds have led to tornado warnings, flooding, and increased fire risks. While these phenomena can provide necessary water resources, they also present substantial dangers, highlighting the need to acknowledge and address climate change impacts on the state’s future weather stability.
Original Source: halifax.citynews.ca