2024 Sees Global Temperature Rise Above 1.5°C Pre-Industrial Levels
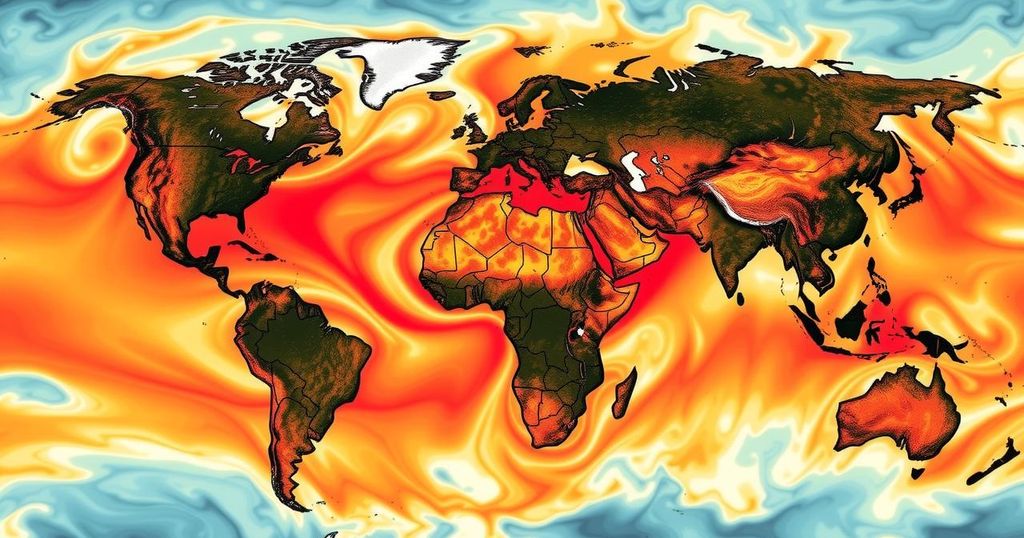
In 2024, global temperatures surpassed the 1.5°C pre-industrial threshold, highlighting the severe impact of climate change. Driven by a powerful El Niño and human-induced factors, extreme weather events, including heatwaves and floods, affected numerous regions, particularly in Europe and Asia. Experts warn that every fraction of a degree in temperature rise increases the risk of irreversible climate damage, necessitating urgent action to mitigate emissions and adapt to extreme conditions.
The year 2024 has marked a significant and troubling milestone, as the global average temperature surged past 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels for the first time, as reported by the European Union’s Copernicus Climate Change Service. Although this temperature spike does not indicate a breach of the Paris Agreement’s long-term limits, it highlights the alarming and escalating consequences of climate change. Influenced by a formidable El Niño and human-induced warming, the world experienced unprecedented heatwaves, wildfires, and extreme meteorological events, with Europe and Asia particularly affected.
On July 10, a staggering 44% of the planet was subjected to severe heat stress. This drastic rise in temperatures, coupled with elevated atmospheric moisture, triggered catastrophic flooding, such as the floods witnessed in Valencia, Spain. Experts in climate science stress that every increment of temperature is critical, for even slight and transient increases can precipitate irreversible damage, including the loss of ice sheets. To mitigate the risk of prolonged warming and its dire consequences, there is a crucial need for urgent action aimed at curtailing greenhouse gas emissions and adapting to the increasing frequency of adverse climate conditions.
The rising global temperatures have been a topic of profound concern among scientists and policymakers. The 1.5°C threshold established in the Paris Agreement serves as a critical point beyond which the impacts of climate change become exceedingly severe. Exceeding this threshold raises questions about the efficacy of current measures to combat climate change, reflecting the need for intensified efforts to prevent further temperature rises. The role of natural phenomena like El Niño and anthropogenic factors in exacerbating climate conditions is significant, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of climate systems and the urgency of mitigation strategies.
In conclusion, the unprecedented rise in global temperatures above the 1.5°C limit in 2024 serves as a stark reminder of the urgent and escalating crisis posed by climate change. The pronounced effects seen in extreme weather patterns, including heat stress and catastrophic flooding, emphasize the critical need for immediate and decisive action to reduce emissions and adapt to the shifting climate landscape. As the scientific community continues to sound the alarm on this pressing issue, the call for coordinated global efforts to combat climate change has never been clearer.
Original Source: www.africa.com






